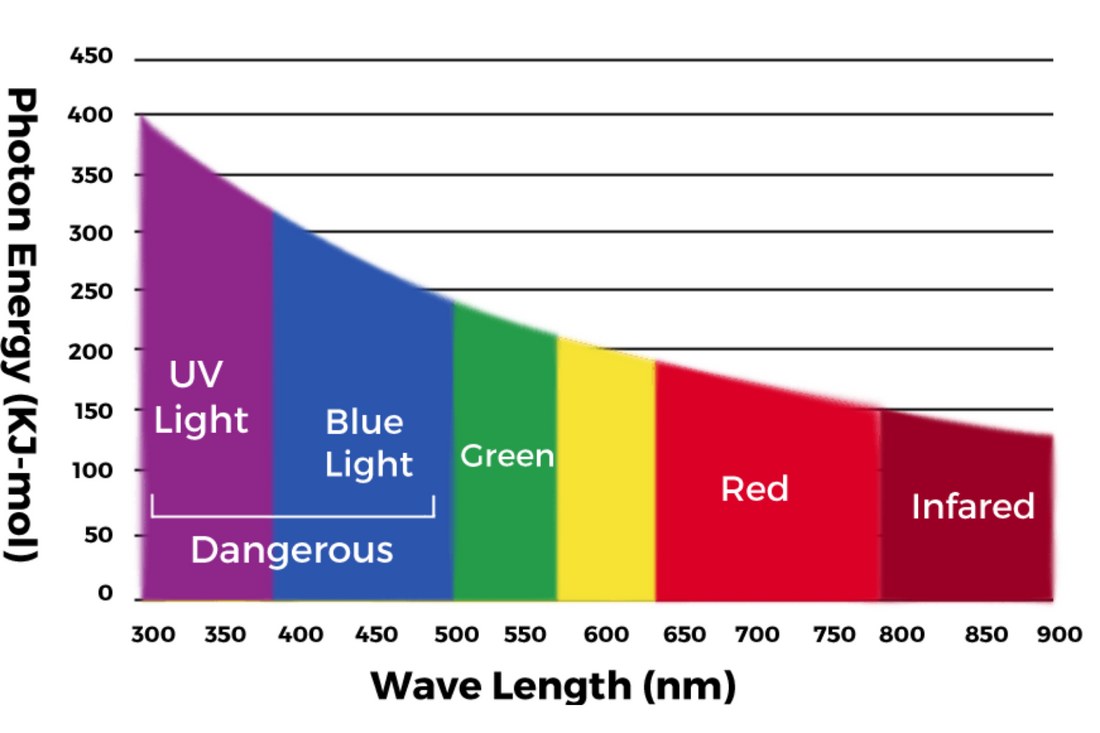
Blue Light and Your Brain
We humans are a funny bunch. During the day, there is this awesome light source burning in the sky but most of us are holed up in offices with electric lights for illumination. As soon as we venture out into natural sunlight, we immediately reach for the sunglasses to protect our precious orbs. Then at night, what do we do? We bare those same eyes to the artificial blue light pulsing from all manner of man-made gadgets – laptops, tablets, TVs and cell phones.
We’ve got it all backwards. The sun has been around for a lot longer than we have so it stands to reason that if we have survived for millennia without sunblock, floppy hats and sunglasses, the sun really isn’t the problem. Truth is, we should all be wearing blue light blocking lenses at night and skip the sunglasses during the day. If you have ever asked yourself “Do I need computer glasses?” read on.
Ample research has shown that we need sufficient exposure to bright light during the day just as we need complete darkness at night. This contrast of a lot of light with a lack of light helps us sleep better and deeper because our internal clocks work more efficiently when they are synchronized with the rhythms of nature.
Light from fluorescent and incandescent bulbs, LEDs (light-emitting diodes) in televisions, smartphones and computers and even the flashing light from an alarm clock all emit blue light which tells your body that it’s still daytime. That’s fine when it is still day time but when it isn’t, your brain and body get thrown off kilter. Anti bluelight glasses help to mitigate these effects by allowing you to see what you are doing without disrupting hormonal cues.
Why? It turns out that our eyes are exquisitely sensitive to blue light, thanks to melanopsin retinal ganglion cells, or mRGCs for short – only recently discovered in 1998. These cells are photoreceptive but originally not thought to be connected to vision. They travel directly to the SCN, or suprachiasmatic nucleus – I can’t pronounce it either - a tiny bunch of cells nestled in the hypothalamus. This represents your body clock and tells you when you need to sleep and when you need to wake up.
The mRGCs therefore regulate our circadian rhythms and certain hormones as well as cycles of sleep and alertness. They also control cognition and pupil size – keep this in mind, I’ll be getting to it later. We now know that blue light at night messes with the production of melatonin, the hormone that makes you feel sleepy and want to go bed. It also delays REM sleep - the deep restorative sleep that helps you heal. If you don’t get enough good quality sleep on a regular basis, you can expect the rest of your life to go to hell in a handbasket. Your brain and body can’t detoxify or rejuvenate properly when good sleep is absent.

Your Brain on TV
What I wanted to know was does blue light affect us in other ways. In the interests of science, I watched a disturbingly depressing doccie made way back in 1995. It’s only about eight minutes long, there’s absolutely no dialogue (just creepy background music) and there is but a single focus of attention – the eyes and faces of a handful of children aged about four or five. Now as rivetingly interesting as this all must sound, bear with me.
So, in this excruciatingly long eight minutes, you can see that all the children are there physically but it’s clear that their little brains are out to lunch. Every one of them has a vacuous, zoned-out expression, as if they are in a coma with their eyes wide open. Their pupils are all enlarged (if you were paying attention, this is a clue) and they look like small zombies who, having recently escaped from the nearest mental institution, decided to sit down and veg out for a while. What were they doing? Watching Disney’s Dumbo on a television screen. Oh and the documentary is called “EVIDENCE” by Godfrey Reggio.
Digging a little deeper, I came across a man called Herbert Krugman who demonstrated that 30 seconds of watching TV was all it took to induce an alpha state in the brain. Using an EEG machine, he found that when his subject picked up a magazine and started reading, her brain returned to Beta. Let’s take a quick tour of brain waves before we continue.
Brain Waves in short
Brain waves are nothing if not confusing and complex but to give you a very short rundown, they are categorized into five broad categories. At any one time, all five are present but in varying degrees. Delta waves are associated with deep sleep and the unconscious mind and have the slowest frequency. Blue light in the evening is known to disrupt the production of Delta waves later on in the night.People who struggle to fall asleep or who wake up during the night might experience "Alpha intrusion sleep disorder" where they are suddenly roused from sleep and feel way more alert than they should be but they aren’t quite awake enough to make sense of anything.
The fastest frequency is created by Gamma waves but we don’t know a whole lot about them except that they involve the entire brain and accompany pure, altruistic thought and genius. In between these two are Theta (sleep, deep meditation, inspiration and dreaming), Alpha (meditative, resting brain state) and Beta (focused, problem solving state).
Beta waves dominate when you are paying conscious attention, i.e. thinking. In Alpha, you are still paying attention but it’s more of a trance like, relaxed and open minded kind of attention where you are not using any critical thinking skills. It’s the day dreamy twilight zone between the subconscious mind and conscious awareness. Alpha is expansive and out of focus, so details don’t’ matter too much and you are in a highly suggestible frame of mind. People with ADD typically exhibit more dominant Alpha and Theta waves and an inability to maintain Beta waves.
Getting back to the television, when you tune into it, your logical brain tunes right out. This means you are exposed to accepting whatever messages are being broadcast because your mind is not focusing on the details. The scary part is the blue light admitted by TV enlarges your pupils so it’s like a double whammy – your eyes are wide open but your brain isn’t. You are on auto-pilot with no one sitting in the cockpit. If you are thinking mind control, manipulation and subliminal seduction right now, you would be right.
Our man Krugman also showed that when watching television, the right side of the brain was engaged twice as much as the left and that endorphins were released. The right is the more imaginative, emotional side whilst the left tends to be more analytical. The right hemisphere also has no sense of time, which explains how you can lose hours watching TV and not notice.
As reported in The Perfect Machine by Joyce Nelson, Krugman wrote, “It appears that the mode of response to television is more or less constant and very different from the response to print. That is, the basic electrical response of the brain is clearly to the medium and not to content difference.... [Television is] a communication medium that effortlessly transmits huge quantities of information not thought about at the time of exposure.”
Well, ain’t that great. He also said, “The time may come when the mass media may create special programs to help people modify certain attitudes or behavior.” If you think this might happen sometime in the future so you still have time to prepare yourself, think again. Krugman said this around 1969.
Yup, almost half a century ago they knew that television was a pervasive influence and represented a unique opportunity to shape the public mindset. Just so you know, Krugman became corporate manager of public-opinion research for General Electric (GE) in 1967. This is the same company that founded the Radio Corporation of America in 1919 and later the National Broadcasting Company (NBC) and also bought a majority share of Universal Pictures in 2004.
TV is primarily a visual experience with sound being the secondary experience. TV is like the gateway drug of technology because it has primed us to readily adopt computers, smart phones, tablets and social media as its natural extensions. It has been called the “plug in drug” and the “fast food” of media. In the US today, children as young as three months old are plonked in front of this electronic babysitter daily. Older children attend school for approximately 40 hours a week and then spend the same amount of time in front of the television.
What’s the solution? Get rid of your TV, read books, engage with your children, go to the museum or the park and get blue light glasses for all the other tech in your house.
