
Your Guide to Screen Time and Sleep Quality
We’ve all been there. You climb into bed, ready for a good night's rest, but decide to check your phone for "just five minutes." Before you know it, an hour has passed, and you feel more wired than when you started. It’s a frustratingly common ritual that connects millions of us, highlighting the growing tension between our digital habits and our biological need for sleep.
The link between screen time and sleep isn’t just in your head; it's a very real and well-documented challenge of modern life.
The Growing Divide Between Screens and Sleep
That struggle to drift off after scrolling through your phone isn't some personal failing. It’s a widespread issue deeply rooted in our daily routines. We live in an age where screens are practically glued to our hands, essential for everything from work and staying in touch to winding down with a movie. But this constant connectivity comes with a hidden cost, especially when we bring it into the bedroom.
The numbers really put this into perspective. The global average for daily screen time has crept up to around 6 hours and 40 minutes. Think about that. That figure has jumped by more than 30 minutes since 2013 alone, a clear sign of just how intertwined our lives have become with these glowing rectangles. You can dig into more screen time statistics on Exploding Topics if you're curious.
This infographic breaks down exactly how that late-night screen time throws a wrench in our natural sleep process.
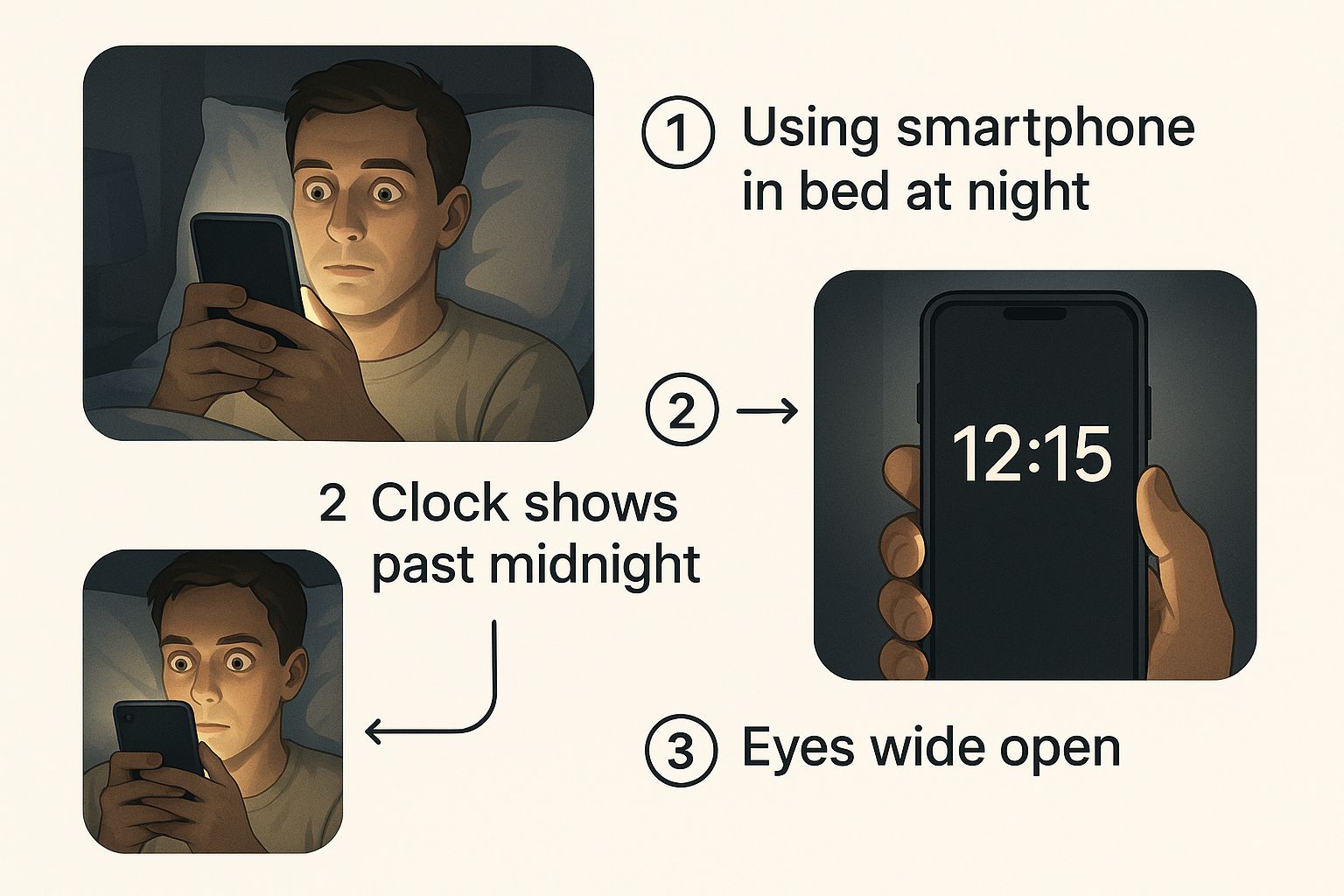
As you can see, the screen's light keeps your mind buzzing and on high alert, long after your body is physically ready to power down. This directly delays the onset of sleep.
Why This Nightly Habit Matters
This pattern of late-night scrolling and streaming creates a major roadblock to getting the quality rest our bodies and minds desperately need. It's not just about losing an hour here and there; when this happens night after night, it can trap you in a cycle of poor sleep and daytime grogginess.
The core issue is that our brains interpret the light from our screens as a signal to stay awake, directly interfering with the natural rhythms that govern our sleep.
Grasping this fundamental conflict is the first real step toward taking back your nights. Once you recognize how screen time messes with your sleep, you can start putting smart strategies in place to find a healthier balance. This guide will walk you through actionable steps to help you break the cycle and start getting better sleep—tonight.
How Blue Light Tricks Your Brain Into Staying Awake
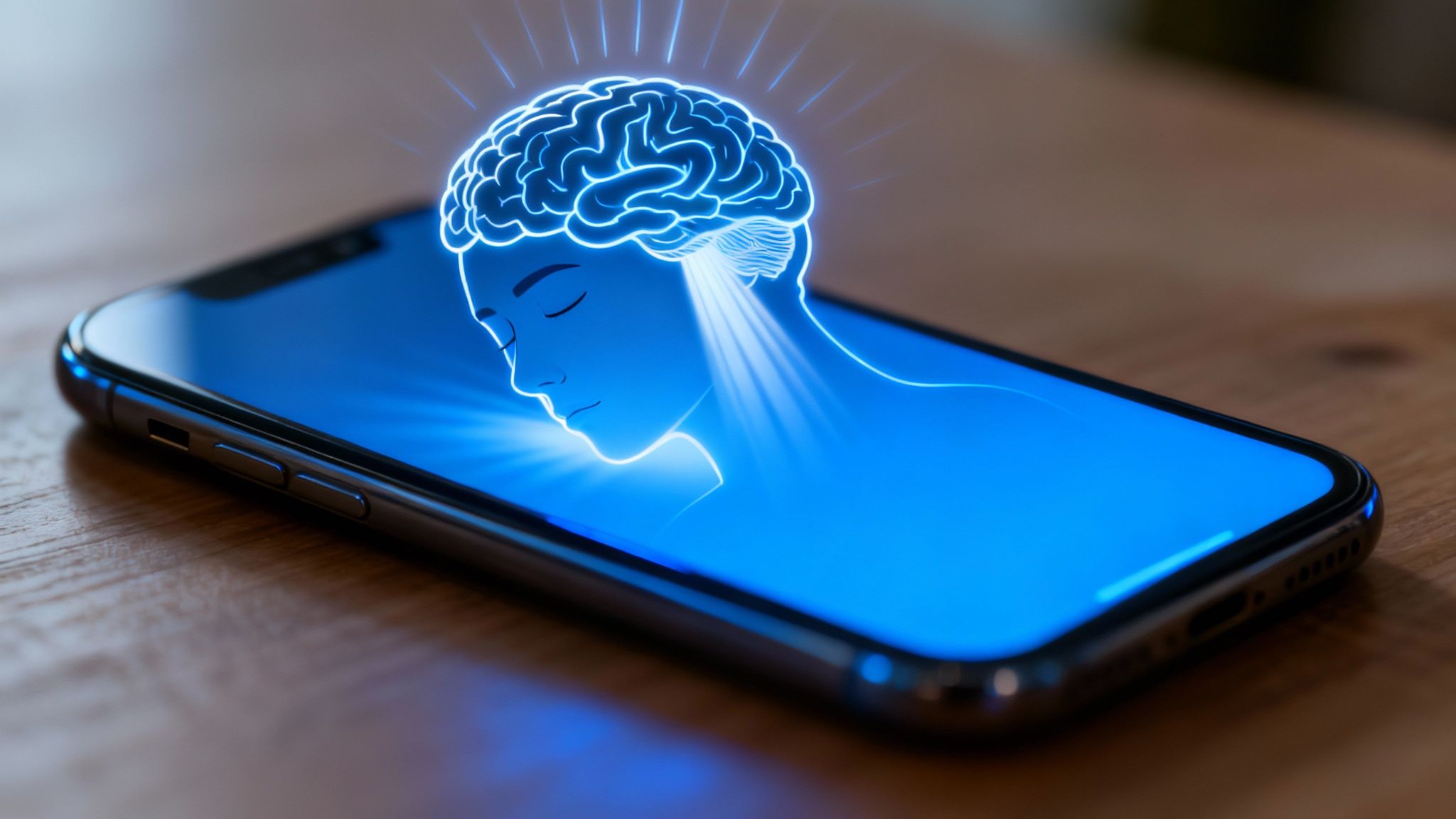

To really get why scrolling your phone at night messes with your sleep, you have to meet your brain’s internal "master clock," also known as the circadian rhythm. Think of it as a super-sensitive manager that runs on a strict 24-hour cycle. It's in charge of telling your body when to feel awake, when to get hungry, and—most importantly—when it’s time to power down for sleep.
For basically all of human history, this system has relied on one main signal from the outside world: light. It was a perfect setup. The bright, powerful light of the sun meant "daytime," keeping us sharp and alert. The slow fade to darkness meant "nighttime," kicking off the body's entire wind-down process.
The Melatonin Switch
Once your eyes start to perceive darkness, your brain flips a pretty critical biological switch. This gives the pineal gland the green light to start producing melatonin, which you've probably heard called the "hormone of darkness."
Now, melatonin isn't like a sleeping pill that just knocks you out. It’s more subtle. It sends a gentle but persistent memo to every cell in your body that it's time to get ready for rest.
As those melatonin levels climb, you start feeling drowsy. Your body temperature dips a bit, your breathing slows down, and your mind finally starts to quiet down. It's your body's natural, incredibly effective way of shifting gears into a deep, restorative sleep.
But this is exactly where our modern gadgets throw a massive wrench into this ancient, finely-tuned machine. The screens on our phones, tablets, and laptops blast out a powerful, high-energy light that directly interferes with this whole process.
How Blue Light Mimics Daylight
Here's the thing: not all light is the same. The light coming from our digital devices is packed with blue wavelengths—the very same kind of light that's strongest in bright, midday sunshine. When your eyes soak up all this artificial blue light in the evening, your brain gets a really confusing signal.
It basically thinks the glow from your screen is daylight, fooling your internal clock into believing it’s still the middle of the afternoon.
In response to this fake "daylight," your brain slams the brakes on melatonin production. That hormone you desperately need to feel sleepy gets shut down, leaving you feeling wired right when you should be winding down.
This biological trickery is the real reason why a little late-night scrolling can leave you staring at the ceiling for hours. Your body is physically tired and ready for sleep, but your brain, duped by the blue light, is stuck in full-on daytime mode.
The fix isn't just about having more willpower; it's about taking back control of your light environment. While setting a "digital curfew" is a great idea, it isn't always realistic. For those times you need to be on a screen after sundown, wearing blue light filtering glasses is a total game-changer.
High-quality eyewear, like PROSPEK glasses, is specifically engineered to block the most disruptive wavelengths of blue light. By putting them on, you help shield your melatonin production, letting your body's natural sleep signals do their job, even while you’re still logged on. It's a simple step that helps bridge the gap between our digital lives and our biological need for a great night's sleep.
The Hidden Health Costs of Screen-Induced Sleep Loss
Feeling a bit groggy after a night of scrolling is just the tip of the iceberg. We all know the immediate effects of a bad night's sleep, but the long-term consequences of consistently sacrificing rest for screen time can take a serious toll on your overall health.
When late-night device use becomes a habit, it messes with more than just your bedtime; it throws your entire sleep architecture out of whack. This constant disruption is a direct pathway to more significant health issues, creating a cycle of poor rest that can feel impossible to break.
The real danger isn't losing an hour of sleep here and there. It's the cumulative effect of chronic sleep debt, which chips away at your physical resilience and mental well-being over time.
This isn't just a minor inconvenience, either. Research shows a powerful link between after-hours screen use and serious sleep problems. For instance, a major study of over 45,000 university students found that for every extra hour of screen time after hitting the sack, the odds of experiencing insomnia symptoms jumped by a staggering 59%. That same hour also shaved off about 24 minutes of their total sleep. You can check out the full study on Frontiers in Psychiatry.
The Ripple Effect on Your Body and Mind
Sleep isn't just a passive state—it's an active process where your body and brain perform essential maintenance. When screens consistently interrupt this vital work, the consequences ripple through your entire system.
Chronic sleep loss is tied to a whole host of wellness concerns, including:
- Weakened Immune Function: Without proper rest, your body produces fewer infection-fighting cells. This leaves you far more vulnerable to getting sick from common bugs.
- Increased Anxiety: A tired brain is often a more anxious one. Sleep deprivation can actually amplify the brain's anticipatory reactions, cranking up feelings of worry and stress.
- Reduced Cognitive Performance: From cementing memories to solving problems, your brain's performance takes a nosedive. You might notice brain fog, difficulty concentrating, and much slower reaction times.
This is especially true for adolescents. Their developing brains are highly sensitive to sleep disruption, and their high screen time is frequently linked to a greater risk of mood disorders and struggles in school. To really get a handle on why this happens, it's worth diving into the intricate science behind sleep cycles and their profound impact on your health.
Ultimately, managing your screen time before bed is about much more than just feeling rested—it's about safeguarding your long-term health from these hidden costs.
Actionable Strategies to Protect Your Sleep

Knowing how screens mess with your sleep is one thing, but actually taking back control of your nights is where the real magic happens. The good news? You don’t need to go on a full-blown digital detox to see a difference. It’s all about creating a healthier balance with a few practical, easy-to-start habits.
The goal is to send your brain a clear signal: the day is over, and it's time to power down. This means creating a buffer zone between your screen-filled day and your quiet, restorative night. By consciously managing your evening routine, you can dial down the negative effects of screen time and sleep quality in a big way.
Establish a Digital Sunset
Just like the setting sun tells the natural world it's time to rest, you can create your own "digital sunset" to signal the same thing to your brain. This is easily one of the most powerful habits you can build.
Make a commitment to turn off all screens—your phone, tablet, laptop, and TV—at least 60 to 90 minutes before your head hits the pillow. Use this tech-free window to do something genuinely relaxing. This might also be a great time to lean into other calming rituals, like incorporating sleep-enhancing candles into your nightly ritual.
This period of disconnection does two crucial things: it stops the flood of new information into your brain and gives your natural melatonin levels a chance to rise, setting you up for a much deeper sleep.
Your bedroom should be a sanctuary for sleep, not an extension of your office or entertainment center. Making it a tech-free zone is a powerful way to reinforce this association in your mind.
If you absolutely must have your phone in the room, at least put it on the other side of the room and flip on "do not disturb" mode. Out of sight, out of mind.
Use Your Device’s Built-In Tools
Most phones and laptops now come with features designed to take the edge off evening blue light exposure. While they aren't a silver bullet, they definitely help.
- Night Mode/Night Shift: This feature automatically warms up your screen's color temperature after sunset, shifting from harsh blues to softer yellows and oranges. This cuts down on the most stimulating light.
- Dark Mode: Switching your apps to a dark background with light text is much less jarring in a dim room. It reduces the overall screen glare and can help with eye strain.
- Grayscale: For the truly committed, turning your screen to black and white is a game-changer. It makes apps, especially flashy social media feeds, far less engaging and easier to put down.
The Ultimate Defense: PROSPEK Glasses
Let's be realistic—completely disconnecting every single night isn't always possible. Maybe you have one last work email to send, or you just want to unwind with an e-book or a show. This is where a quality pair of blue light filtering glasses becomes your best friend.
Computer glasses, like those from PROSPEK, are engineered to filter out the specific wavelengths of blue light that wreak havoc on your sleep cycle. Wearing them in the evening is like putting up a protective shield for your eyes. The artificial light from your screen is blocked from tricking your brain into thinking it's still daytime.
This allows your body to produce melatonin right on schedule, even if you’re still logged on. If you're curious about the science, you can learn more about how blue light glasses can improve your sleep. Think of them as the perfect tool to sync your modern digital life with your body's ancient sleep rhythm.
Your Digital Wind-Down Routine
Creating a structured routine is the best way to make these habits stick. Here’s a simple, step-by-step plan you can adapt to build a screen-free buffer before bed.
| Time Before Bed | Action Item | How It Improves Sleep |
|---|---|---|
| 90 Minutes | Final Screen Check: Wrap up any last emails or messages for the night. | Prevents late-night stress and the temptation to check "just one more thing." |
| 60 Minutes | Screens Off: Power down all devices—phone, TV, laptop. Put your phone away. | Kicks off your "digital sunset," allowing natural melatonin production to begin. |
| 45 Minutes | Relaxing Activity: Read a physical book, listen to music, or stretch. | Shifts your brain from active problem-solving to a calm, restful state. |
| 15 Minutes | Prepare for Sleep: Dim the lights, brush your teeth, and get comfortable. | Sends final, clear signals to your body that it's time for bed, reinforcing your routine. |
Following a simple plan like this helps transition your mind and body from a state of high alert to one of deep relaxation, paving the way for a night of truly restorative sleep.
It's Not Just Blue Light: How Screens Keep You Wired
While blue light gets most of the blame when we talk about screen time and sleep, it's really only part of the problem. What we're actually doing on our devices is just as powerful at keeping us wide awake, kicking our brains into high gear right when they should be winding down.
Just think about it for a second. Your brain doesn't really know the difference between a real-world threat and a psychologically stressful one. That urgent work email, a heated argument on social media, or the last few heart-pounding moments of a video game can all set off the same internal alarms. This kind of mental and emotional stimulation triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
These are the exact same hormones that power your body's "fight-or-flight" response. Their job is to make you sharp, focused, and ready for action—the polar opposite of the calm, relaxed state you need to drift off to sleep.
Engineered to Keep You Hooked
It's not just the content we choose to watch or read. The very design of our favorite apps and websites is built to capture our attention and hold it for as long as possible. App developers are experts in psychological engagement, and they use specific tricks to keep you scrolling, tapping, and watching long after your intended "five minutes" are up.
This isn't by accident; it's by design. These features create a compelling, and sometimes addictive, loop that makes it incredibly difficult to just put the phone down.
Some of the key tactics include:
- Infinite Scroll: By completely removing any natural stopping point, platforms like Instagram and TikTok encourage you to just keep going. There’s always another video or post waiting just a swipe away.
- Push Notifications: Those little pings and pop-ups are designed to create a sense of urgency, pulling your attention right back into an app to see what you might have missed.
- 'Fear of Missing Out' (FOMO): Social media feeds tap directly into our basic human desire to stay connected and in the loop, making us feel like we'll be left out if we sign off.
This constant flood of stimulation doesn't just eat up your time; it actively sabotages your body's natural wind-down process. It's like sending your brain to the gym for a high-intensity workout right before bed, leaving you feeling wired and restless even if your body is exhausted.
This mental overstimulation, paired with the physical strain on your eyes from focusing on a bright screen, can lead to a whole host of discomforts. If you frequently get headaches or find your vision gets blurry after a long screen session, you can learn more by unpacking computer vision syndrome symptoms in our detailed guide. Getting a good night's sleep means managing both the light coming from your screens and the stimulating content they deliver.
Building a Healthier Relationship with Your Tech
Reclaiming your sleep from screen time isn’t about a few quick fixes; it's about playing the long game. The real win is building sustainable digital habits that stick, leading to better sleep and just feeling better overall. This means moving beyond temporary band-aids and creating a more intentional, balanced relationship with your devices.
Think of it like setting healthy boundaries in any other relationship. Just as you need personal space from people, your mind needs a break from constant digital chatter, especially as you wind down for bed. This is where creating tech-free zones becomes a surprisingly powerful strategy for helping your screen time and sleep coexist peacefully.
Create Screen-Free Sanctuaries
Making certain areas of your home "screen-free"—especially the bedroom—sends a powerful signal to your brain. It reinforces that the bedroom is a sanctuary for rest and intimacy, not for work emails or doomscrolling. An easy first step? Start charging your phone in another room overnight.
Another great strategy is to schedule dedicated time away from your devices. This could be the first hour after you wake up or even a full "digital Sabbath" one day a week. The goal is to be more mindful and intentional with your technology, putting you back in the driver's seat instead of letting it control you.
A healthier relationship with technology isn't about complete avoidance. It’s about conscious engagement, where you decide how and when screens fit into your life, ensuring they serve you without disrupting your rest.
This is especially critical for kids and teens. We're seeing more and more that high screen time among adolescents is linked to poor sleep quality and other health issues. In fact, research shows that teens with heavy daily screen use are more likely to have erratic sleep schedules and be less physically active. You can discover more about these findings from the CDC.
By setting these boundaries, you’re not just trying a new trick; you're building lasting strategies for a healthier life. If you're looking for more practical advice, check out our guide on how to limit screen time.
Your Top Questions About Screens and Sleep, Answered
When you start digging into the connection between screen time and sleep, a few common questions always pop up. Let's tackle them head-on with some straightforward answers to help you get your sleep schedule back on track.
Is Night Mode Enough to Protect My Sleep?
While features like Night Mode and Dark Mode are a decent starting point, they're far from a complete fix. These settings work by warming up the color temperature on your screen, which does reduce some blue light and can take the edge off its impact on melatonin. But here's the catch: they don't block it completely.
Besides, it's not just about the light. What you're looking at matters, too. A stressful work email or a thrilling video clip can send your brain into high alert, making it tough to wind down no matter what color your screen is. Think of these modes as a helpful first step, but not a magic bullet for late-night screen habits.
How Can I Help My Child or Teen with Their Screen Time Habits?
This is a big one, because kids and teens are even more sensitive to blue light's effect on their internal clocks. The key here is creating clear, consistent boundaries.
- Declare a "digital curfew." Have all screens turned off at least an hour before their official bedtime.
- Create a central charging spot. Make sure this is outside of their bedrooms, so there's no temptation for late-night scrolling.
- Lead by example. The most powerful tool you have is modeling good behavior by putting your own phone away.
If your teen absolutely has to use a device for late-night homework, a good pair of blue light filtering glasses can be a real game-changer. Brands like PROSPEK glasses even make styles specifically for younger faces, helping to protect their melatonin production while they wrap up their assignments.
Do Blue Light Glasses Actually Work for Sleep?
Yes, and the science backs it up. When you wear quality blue light blocking glasses, such as those from PROSPEK, in the evening, they can make a real difference in your sleep.
By filtering out the specific wavelengths of blue light that mess with your internal clock, they stop your brain from getting the "hey, it's still daytime!" signal. This allows your body to produce melatonin on its natural schedule, helping you feel sleepy when you're supposed to and ultimately improving the quality of your rest.
Ready to stop blue light from hijacking your sleep? See how Spektrum Glasses can help you unwind the natural way, even when you need to stay plugged in. Explore our collection of scientifically-engineered blue light filtering glasses today.
